A place for everything and everything in its place. Curiously, this saying captures what office management is all about. But there's much more to it than just organizing invoices and keeping spreadsheets up to date.
Office management involves project management, space management, people management, time tracking, and everything else that improves efficiency, boosts productivity, and enhances collaboration in the office. It's a lot more complex than it appears at first sight! That's why understanding the essentials of office management is critical for facility professionals and anyone looking to streamline office operations.
In this guide, we'll dive into the art of effective office management. Join us and explore what it entails, its benefits, and some practical tips on excelling in the field.
TL;DR:
- Office management involves planning, organizing, staffing, directing, controlling, and coordinating to ensure workplace efficiency.
- Effective office management boosts productivity, improves collaboration, and streamlines operations beyond just administrative tasks.
- Key office management roles vary across corporate, legal, medical, and virtual environments, each with specialized responsibilities.
- Successful office managers combine education, technical proficiency, leadership, problem-solving, and communication skills.
- Efficient office management reduces costs, enhances productivity, improves employee morale, and strengthens workplace culture.
- Modern trends like hybrid work, technology integration, and data-driven decision-making are reshaping office management strategies.
- Major challenges include communication gaps, maintaining culture, technology access, and optimizing hybrid workspaces.
- Best practices include structured organization systems, financial discipline, continuous improvement mechanisms, and smart technology adoption.
What is Office Management?
Office management is the systematic planning, organizing, and control of business operations, equipment, information, and human resources to facilitate the achievement of organizational goals. It serves as the backbone of organizational operations, ensuring all elements work together harmoniously to create an efficient and productive work environment.
Effective office management extends beyond basic administrative tasks to include strategic planning, resource allocation, communication facilitation, record-keeping, and optimizing work environments. It's the operational framework that enables employees to perform at their best by providing the structure, tools, and support they need to excel in their roles.
As Hunter Muller, CEO of HMG Strategy, emphasizes: "Technology leaders have a unique opportunity right now to drive the enterprise forward… technology leaders are in a career-defining moment." This perspective highlights how modern office management has evolved from an administrative function to a strategic driver of organizational success.

The 6 Key Functions of Office Management
Understanding the six fundamental functions of office management provides a comprehensive framework for organizing and optimizing workplace operations:
Planning
Planning forms the foundation of effective office management by establishing clear objectives, strategies, and action steps. This function involves forecasting future needs, setting measurable goals, and developing comprehensive roadmaps for achieving those goals.
Practical Implementation:
- Create quarterly planning templates that align departmental objectives with organizational goals
- Implement weekly team planning sessions to set priorities and allocate resources
- Develop contingency plans for common operational disruptions
Companies implementing structured planning processes report 20% higher productivity compared to those with ad-hoc approaches.
Organizing
Organizing translates plans into actionable structures by establishing systems, processes, and frameworks that facilitate efficient operations. This function involves creating logical workflows, defining clear roles and responsibilities, and developing organizational hierarchies.
Practical Implementation:
- Document standard operating procedures for common office tasks
- Create clear responsibility matrices for cross-functional projects
- Implement digital organization systems that mirror physical filing structures
Staffing
Staffing focuses on human resource management within the office environment, ensuring that the right people with the appropriate skills are in place to support organizational objectives.
Practical Implementation:
- Develop skills inventories to identify organizational capabilities and gaps
- Create cross-training programs to ensure operational continuity
- Implement structured onboarding processes that reduce time-to-productivity
Organizations with comprehensive staffing strategies report 15% higher retention rates and see corresponding boosts in productivity.
Directing
Directing involves providing leadership, guidance, and supervision to ensure that plans are executed effectively and that staff members remain motivated and aligned with organizational goals.
Practical Implementation:
- Schedule weekly one-on-one coaching sessions with team members
- Implement visual management systems that provide clear performance feedback
- Create decision-making frameworks that empower appropriate autonomy
Controlling
Controlling ensures that operations proceed according to plan by establishing performance standards, monitoring actual performance, and implementing corrective actions when necessary.
Practical Implementation:
- Develop dashboards that track key performance indicators
- Schedule monthly variance analysis reviews to identify improvement opportunities
- Implement quality control checklists for critical operational outputs
Coordination
Coordination integrates all other management functions by ensuring that different departments, teams, and individuals work together harmoniously toward common goals.
Practical Implementation:
- Establish cross-functional working groups for key initiatives
- Implement communication protocols that ensure information flows appropriately
- Create shared calendars and resource scheduling systems
Office Management Function Implementation Template:
|
Function |
Key Activities |
Implementation Tools |
Success Metrics |
|
Planning |
Goal setting, resource allocation |
Project management software, planning templates |
% of objectives completed on time |
|
Organizing |
Process documentation, system creation |
Document management, workflow tools |
Time saved through standardization |
|
Staffing |
Recruitment, training, development |
Skills matrices, training platforms |
Employee competency scores, retention rates |
|
Directing |
Leadership, motivation, guidance |
Meeting structures, feedback systems |
Employee engagement scores |
|
Controlling |
Standard setting, performance monitoring |
KPI dashboards, quality checklists |
Variance from standards, error rates |
|
Coordination |
Information sharing, conflict resolution |
Communication platforms, shared calendars |
Cross-departmental project success rates |
Types of Office Management Roles
Office management encompasses various specialized roles across different industries, each with unique responsibilities tailored to specific organizational needs:
Corporate Office Management
Corporate office managers oversee administrative operations in business environments ranging from startups to multinational corporations. They typically handle a broad range of responsibilities including facilities management, vendor relations, administrative team supervision, and executive support.
Legal Office Management
Legal office managers specialize in administrative oversight within law firms and legal departments, where they must navigate unique compliance requirements and confidentiality protocols. Their responsibilities include case file management, legal billing coordination, court filing systems, and maintaining attorney schedules.

Medical Office Management
Medical office managers coordinate administrative functions in healthcare settings such as medical practices, clinics, and hospitals. Their specialized responsibilities include patient scheduling, insurance verification, medical records management, and healthcare compliance monitoring.
Virtual Office Management
Virtual office managers coordinate distributed teams and remote operations, often working with team members across multiple time zones and locations. This emerging role focuses on digital coordination, online communication systems, virtual meeting facilitation, and digital document management. With approximately 87% of organizations worldwide now operating with a hybrid work model, virtual office management has become an essential capability rather than a specialized niche.
The Role and Qualifications of an Office Manager
Office managers serve as the operational backbone of organizations, combining administrative expertise with leadership skills to ensure smooth workplace functioning. Their multifaceted role encompasses both day-to-day operations and strategic contributions to organizational success.
Core Responsibilities
The office manager's role includes a diverse set of responsibilities:
- Administrative Oversight: Managing office supplies, maintaining equipment, coordinating maintenance, and overseeing general office operations
- Financial Management: Processing invoices, managing petty cash, assisting with budget preparation, and tracking departmental expenses
- Personnel Coordination: Supervising administrative staff, conducting performance evaluations, and facilitating onboarding processes
- Communication Facilitation: Serving as an information hub between departments, executives, and external stakeholders
- Meeting and Event Planning: Coordinating schedules, preparing materials, arranging venues, and managing logistics
- Facility Management: Overseeing office space utilization, security protocols, and workplace safety compliance
Practical Framework: Office Manager Daily Checklist
- Morning: Review daily schedule, prepare for meetings, address urgent emails
- Mid-morning: Conduct facilities walk-through, address maintenance issues
- Noon: Coordinate lunch arrangements, manage visitor check-ins
- Afternoon: Process invoices and financial documents, update inventory systems
- End of day: Prepare next-day meeting materials, secure office areas
Required Qualifications and Skills
Successful office managers possess a combination of educational credentials, technical abilities, and soft skills:
Education and Certifications
Many employers seek candidates with at least an associate or bachelor's degree in business administration, office management, or related fields. Industry-specific certifications enhance credibility and expertise:
- General Office Management: Certified Administrative Professional (CAP) or Certified Manager (CM) credentials
- Medical Settings: Certified Medical Office Manager (CMOM) certification
- Legal Environments: Certified Legal Manager (CLM) designation
Technical Skills
Office managers need proficiency in various technologies and systems:
- Software Expertise: Advanced knowledge of Microsoft Office suite, project management tools, and communication platforms
- Financial Acumen: Budgeting, basic accounting principles, and financial tracking systems
- Data Management: Database administration, record-keeping, and information security protocols
Pedro Bados, CEO of Nexthink, emphasizes the importance of technology skills: "Delight people at work. It is that simple. Companies must create strong digital experiences that delight their employees." This highlights how modern office managers must be digitally fluent to create positive workplace experiences.
Soft Skills
The interpersonal dimensions of the role require:
- Leadership Ability: Motivating teams, delegating effectively, and providing constructive feedback
- Problem-Solving Capacity: Identifying issues, analyzing options, and implementing practical solutions
- Communication Excellence: Clear writing, active listening, and effective verbal communication
- Adaptability: Flexibility in responding to changing priorities and organizational needs
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks effectively and managing multiple responsibilities simultaneously

The Importance of Efficient Office Management
Efficient office management delivers measurable benefits across all aspects of organizational performance, serving as a catalyst for operational excellence and competitive advantage.
Operational Streamlining and Cost Efficiency
Well-designed office management systems eliminate redundancies, automate routine tasks, and optimize resource utilization. This streamlining creates significant cost efficiencies through:
- Reduced administrative overhead through standardized processes
- Decreased waste in supplies and resources through inventory control systems
- Lower operational costs through preventive maintenance and equipment lifecycle management
- Improved space utilization through strategic workspace planning
- Enhanced energy efficiency through mindful facility management
Implementation Tool: Administrative Cost Tracking Template
|
Category |
Previous Cost |
Current Cost |
Savings |
Optimization Method |
|
Office Supplies |
$X |
$Y |
$Z |
Centralized purchasing, inventory control |
|
Software Licenses |
$X |
$Y |
$Z |
Consolidated subscriptions |
|
Space Utilization |
$X |
$Y |
$Z |
Hybrid scheduling optimization |
|
Administrative Time |
$X |
$Y |
$Z |
Process automation |
Productivity Enhancement and Performance Optimization
Effective office management creates environments where employees can focus on high-value work rather than administrative friction, resulting in:
- Faster task completion through optimized workflows and reduced bottlenecks
- Higher quality outputs through standardized procedures and quality control measures
- Increased innovation through systems that free cognitive resources for creative thinking
- Greater work output through elimination of unnecessary steps and processes
- Improved cross-departmental collaboration through coordinated information systems
Measurable Impact: Companies implementing comprehensive benefits and HR management systems have achieved a 30% reduction in onboarding time and lowered administrative costs by 25%.
Employee Morale and Workplace Experience
Office management directly shapes the daily experience of employees, influencing satisfaction and retention through:
- Reduced workplace frustration by eliminating common administrative pain points
- Enhanced professional pride through association with well-run operations
- Greater work-life balance through efficient systems that reduce overtime requirements
- Improved workplace relationships through clear communication protocols
- Stronger organizational culture through consistent application of values in operations
Decision-Making and Strategic Execution
Strong office management provides the operational foundation that enables effective strategic execution:
- More informed decision-making through organized data and reporting systems
- Faster implementation of strategic initiatives through established operational frameworks
- Greater organizational agility through systems designed to adapt to changing needs
- Improved risk management through comprehensive record-keeping and compliance monitoring
- Enhanced leadership effectiveness through reduced time spent on operational troubleshooting
Evolution and Trends in Office Management
Office management practices have undergone significant transformation, reflecting broader changes in technology, workplace culture, and business objectives. Understanding this evolution provides valuable context for implementing effective contemporary strategies.
Historical Development of Office Management
The evolution of office management reflects the changing nature of work and organizational structures:
Early 20th Century (1900s-1940s): Office management emerged as a distinct function during the industrial revolution, heavily influenced by scientific management principles pioneered by Frederick Taylor. Workspaces featured rigid hierarchies, with managers focused primarily on supervision and standardization.
Mid-Century Period (1950s-1970s): As businesses grew more complex, office management evolved to include more sophisticated human relations approaches. The Bürolandschaft concept emerged in Germany, promoting organic office layouts designed to facilitate communication rather than just supervision.
Information Age Transition (1980s-1990s): The introduction of personal computers dramatically changed office management responsibilities. Office managers now coordinated technology implementation alongside traditional administrative functions.
Early Digital Era (2000s-2010s): Internet connectivity fundamentally altered communication patterns and information management in offices. Office managers took on expanded responsibilities for digital security, technology training, and managing remote work capabilities.
Contemporary Trends Reshaping Office Management
Today's office management landscape continues to evolve rapidly in response to multiple factors:
Hybrid Work Model Integration: The most significant current shift in office management involves adapting to hybrid work arrangements that blend remote and in-office work.
Technology-Enhanced Operations: Advanced software solutions now automate many traditional office management functions, from visitor management to resource scheduling. According to CBRE research, 62% of organizations have reduced their office portfolios since 2020, creating a need for more sophisticated space management technologies.
Employee Experience Focus: Modern office management prioritizes creating environments that enhance employee well-being, satisfaction, and productivity. Space sharing has increased by 30%, with collaboration spaces growing by 44% since 2021 as workplaces adapt to hybrid styles.
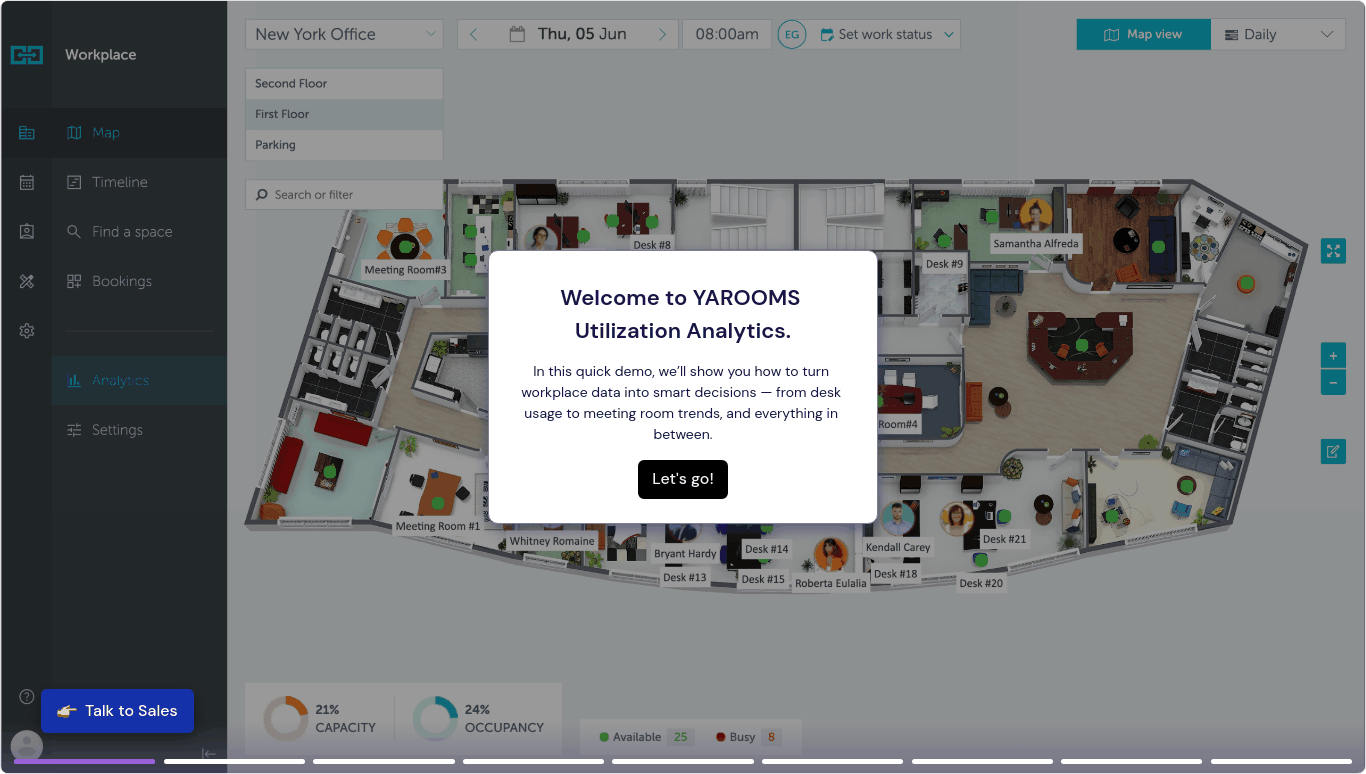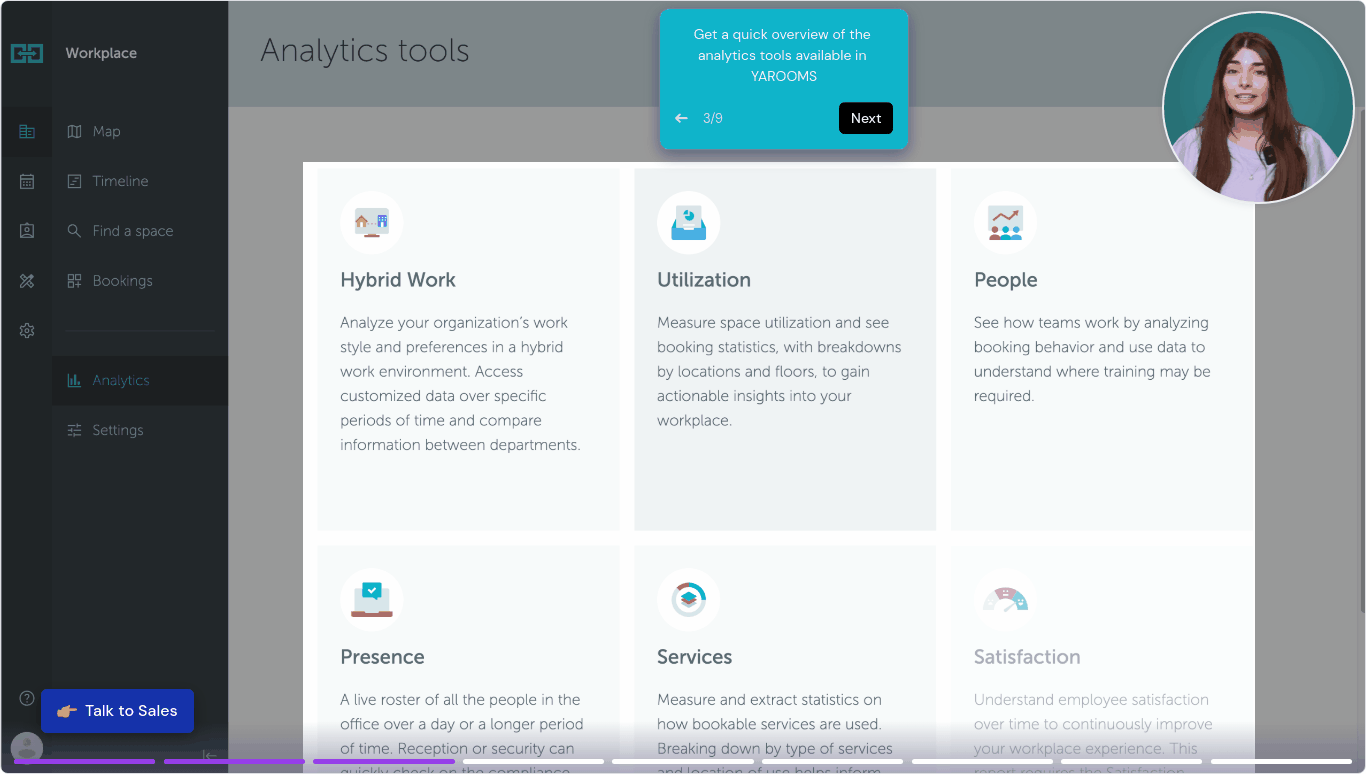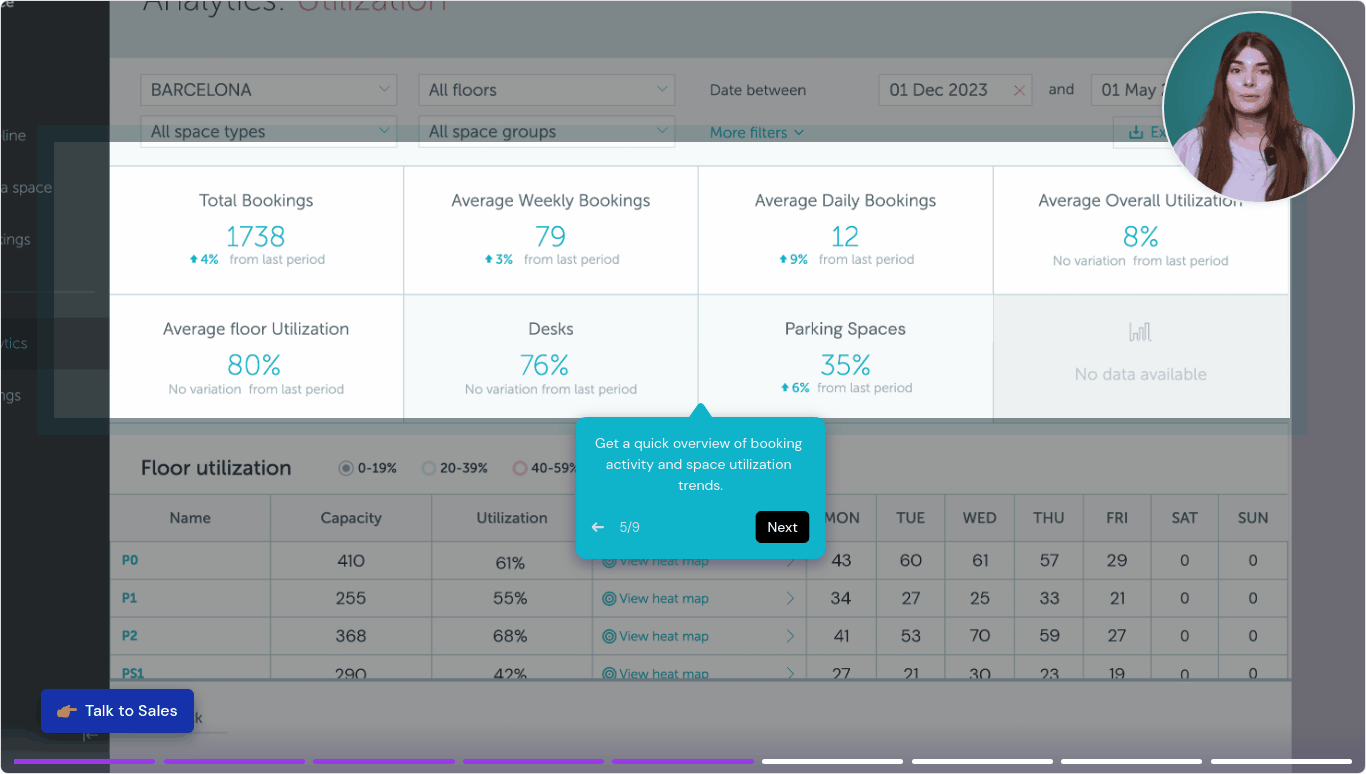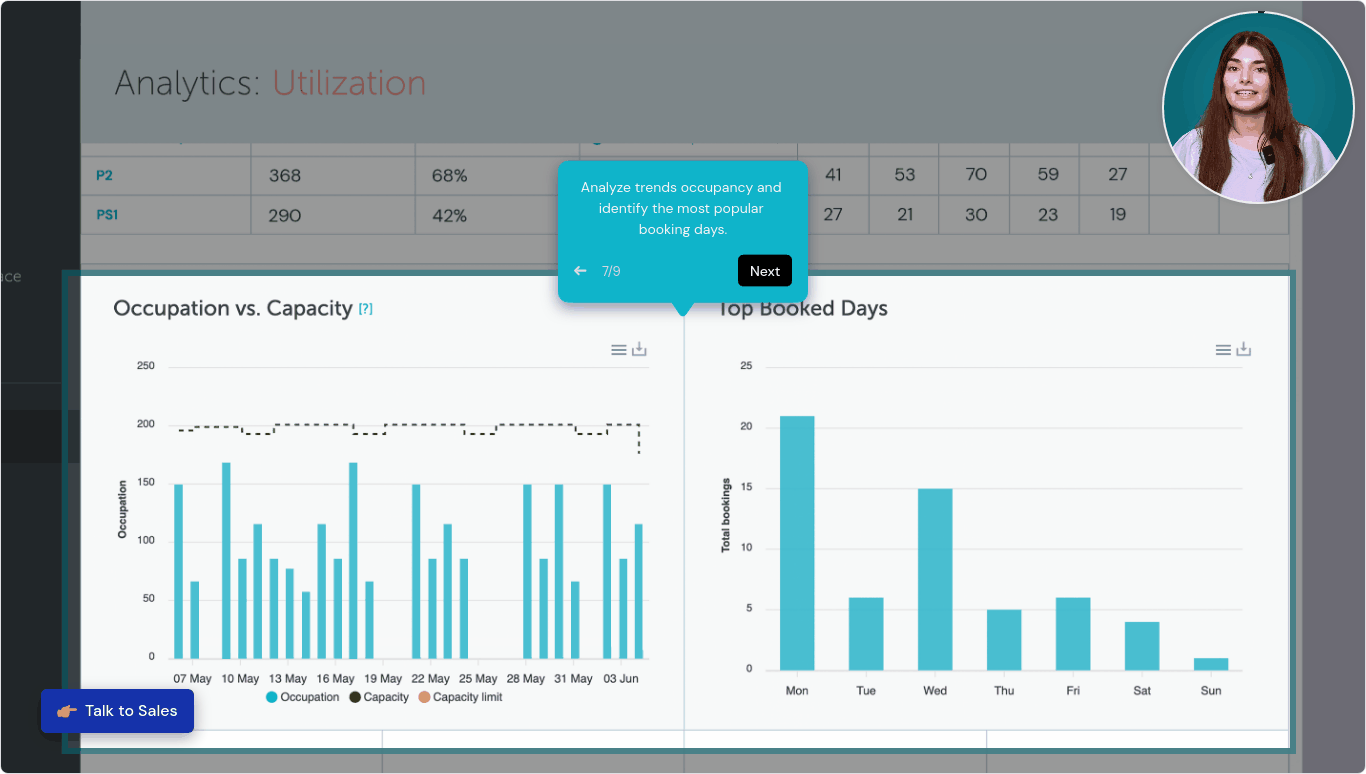
Data-Driven Decision Making: Contemporary office management relies heavily on workplace analytics to optimize operations and resource allocation. According to JLL, 77% of organizations now track space utilization data to inform workplace strategy decisions.
Click on the image to see the YAROOMS workplace analytics in action ⬇️
Challenges in Modern Office Management
Today's office managers face a complex set of challenges, particularly in hybrid work environments that blend remote and in-person operations. Understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions is critical for maintaining operational excellence.
Communication and Collaboration Barriers
Hybrid work environments often create communication silos and collaboration inequities between in-office and remote workers. According to research from Zoom, hybrid employees show higher engagement rates (35%) than fully remote (33%) or fully in-office employees (27%), but only when collaboration barriers are effectively addressed.
Effective Solutions:
- Implement unified communication platforms with clear usage guidelines to ensure all team members have equal access to information
- Establish "digital-first" meeting protocols where all participants connect individually via video, even when some are in the same physical location
- Schedule regular synchronous check-ins complemented by asynchronous documentation to accommodate different work schedules
YAROOMS Solution: The YAROOMS workplace management platform integrates with major communication tools like Microsoft Teams and Zoom, creating seamless connections between space management and virtual collaboration that help bridge the gap between remote and in-office workers.

Maintaining Organizational Culture and Cohesion
Distributed teams often struggle with cultural fragmentation and inconsistent employee experiences. According to Gartner research, lack of explicit hybrid work norms increases the likelihood of employee turnover by 12%, highlighting the importance of intentional culture-building.
Effective Solutions:
- Develop explicit culture documentation that clearly articulates values, expectations, and working norms for all team members regardless of location
- Create inclusive recognition systems that equally highlight contributions from both remote and in-office employees
- Design hybrid-friendly social events that meaningfully include remote participants rather than making them passive observers
Technology Integration and Digital Equity
Hybrid work environments depend heavily on technology, creating challenges around system reliability, digital accessibility, and varying levels of technical proficiency among team members.
Effective Solutions:
- Implement a technology equity policy ensuring remote workers have equipment comparable to office setups, including proper ergonomic furniture and high-quality audio/video tools
- Establish clear technical support protocols with equal response times for remote and in-office issues
- Provide comprehensive digital literacy training focused on collaboration tools and virtual communication skills
YAROOMS Solution: YAROOMS' intuitive mobile app ensures that employees can manage their hybrid work schedules, book resources, and coordinate with colleagues regardless of their location or technical expertise.

Workplace Utilization and Resource Allocation
Traditional office space utilization models become inefficient in hybrid environments, leading to wasted resources and suboptimal experiences. Over the past three years, office space per employee has decreased by 22% globally due to hybrid work models, requiring more sophisticated management approaches.
Effective Solutions:
- Deploy workspace booking systems that provide real-time visibility into office utilization patterns
- Redesign office spaces to emphasize collaboration zones while reducing individual workstations based on attendance patterns
- Implement sensors and utilization tracking to gather data on how spaces are actually being used
Implementing Best Practices in Modern Office Management
Successful office management requires implementing practical, evidence-based strategies across multiple operational dimensions. These best practices serve as the foundation for efficient, productive, and positive workplace environments.
Organization and Efficiency Systems
Effective organization creates the infrastructure for operational excellence in any office environment. Research shows that employees waste up to 30 minutes daily searching for materials in disorganized environments, making systematic organization a high-ROI investment.
Implementation Framework: Office Organization System
1. Audit Current State- Document existing filing systems and information flows
- Identify pain points and inefficiencies through employee surveys
- Map physical and digital storage requirements
- Create consistent naming conventions for files and folders
- Establish clear retention policies for different document types
- Implement parallel physical and digital organization structures
- Provide comprehensive training on new systems
- Schedule phased implementation to minimize disruption
- Designate system champions to support adoption
- Track time saved and user satisfaction
- Identify and address emerging pain points
- Schedule quarterly system reviews
Communication Frameworks
Strategic communication systems prevent information silos and ensure alignment across teams and departments. Organizations with highly effective communication practices are 4.5 times more likely to retain the best employees and significantly outperform competitors in productivity metrics.
Financial Management and Resource Optimization
Disciplined financial oversight ensures operational sustainability and maximizes resource impact. Organizations with strong financial management practices within their office operations typically achieve 15-20% greater efficiency in administrative spending.
Implementation Steps:
- Create comprehensive budget categories that align with operational activities
- Implement approval workflows with appropriate thresholds
- Develop vendor evaluation criteria beyond simple cost comparisons
- Schedule quarterly spending reviews to identify optimization opportunities
Resource Optimization Case Study: A mid-sized marketing agency implemented YAROOMS' desk booking system after discovering their office utilization averaged only 40% on most days. By moving to a hybrid model with hoteling workstations, they reduced their office footprint by 30%, saving approximately $250,000 annually in lease costs while maintaining team cohesion and productivity.
Workplace Technology Integration
Strategic technology implementation streamlines operations and enhances workplace capabilities. Data-backed office management decisions provide actionable insights that significantly improve processes and productivity.
Technology Assessment Framework
|
Technology Area |
Current Capability |
Gap Analysis |
Implementation Priority |
Integration Requirements |
|
Space Management |
Manual spreadsheets |
Limited visibility, no analytics |
High |
Calendar systems, building access |
|
Document Management |
Mixed paper/digital |
Inconsistent access, version control issues |
Medium |
Communication tools, project systems |
|
Meeting Management |
Basic calendar |
No integration with resources, poor visibility |
High |
Space booking, visitor systems |
|
Visitor Management |
Paper log |
Security concerns, poor experience |
Medium |
Building security, notification systems |
Continuous Improvement Mechanisms
Establishing systematic feedback loops creates cultures of ongoing enhancement rather than sporadic change initiatives. Organizations with strong continuous improvement mechanisms typically achieve 3-5% productivity gains annually through incremental optimizations.
Practical Implementation: Office Experience Feedback System
1. Create a quarterly office experience survey covering:- Space functionality and comfort
- Technology effectiveness
- Administrative process efficiency
- Communication effectiveness
- Overall workplace satisfaction
- Review feedback data
- Prioritize improvement opportunities
- Develop and implement action plans
- Communicate changes back to the organization
- Issues identified
- Solutions implemented
- Impact measured
- Upcoming improvements
YAROOMS Solution: YAROOMS' feedback collection tools allow organizations to gather real-time input on space quality, meeting effectiveness, and service requests, creating a continuous improvement cycle for workplace experience.
Office Management Software Solutions
The right software tools significantly enhance office management capabilities, providing automation, insights, and coordination mechanisms that would be impossible through manual processes alone. Understanding the landscape of available solutions helps organizations make strategic investments in technologies that address their specific needs.
Core Functions of Office Management Software
Modern office management platforms typically include several essential capabilities:
Workspace Management: Digital solutions for booking desks, meeting rooms, and other shared resources ensure optimal space utilization while providing employees with visibility and control over their work environment.
Visitor Management: Digital check-in systems streamline the arrival experience for guests while enhancing security through automated notifications, badge printing, and record-keeping. These systems integrate with calendars and meeting room bookings to create seamless experiences for both visitors and their hosts.
Document Management: Centralized document repositories with version control, permission settings, and search capabilities ensure that information is both secure and accessible. These systems typically include workflow features for approvals, electronic signatures, and retention policy enforcement.
Communication and Collaboration: Integrated messaging, video conferencing, and project management tools facilitate coordination across distributed teams. Modern platforms emphasize mobile accessibility, notification management, and integration with other workplace systems.
Analytics and Reporting: Data visualization tools provide insights into space utilization, resource consumption, and operational patterns.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful implementation of office management software requires strategic planning and ongoing optimization:
- Begin with clear objectives: Define specific problems the software should solve and metrics for success before evaluating options. This prevents feature-chasing and ensures alignment with organizational needs.
- Involve end-users in selection: Include representatives from different departments in the evaluation process to ensure the solution addresses diverse needs and use cases.
- Plan phased deployment: Roll out functionality incrementally, starting with high-value, low-complexity features that generate quick wins and build confidence in the system.
- Invest in proper training: Develop role-specific training materials and provide multiple learning formats (documentation, videos, live sessions) to accommodate different learning preferences.
- Establish governance procedures: Create clear policies for system administration, data management, and feature requests to maintain system integrity over time.
Organizations that follow these implementation practices typically achieve 60-80% higher adoption rates than those pursuing ad hoc deployment strategies, significantly increasing their return on technology investments.
Measuring Success in Office Management
Establishing robust measurement systems is essential for evaluating office management effectiveness and demonstrating its strategic value to the organization. This section outlines key metrics and measurement frameworks for comprehensive office management evaluation.

Key Performance Indicators for Office Management
Effective office management measurement combines operational, financial, and experience metrics to provide a holistic view of performance:
Operational Efficiency Metrics
- Process Cycle Time: Measure the duration of key administrative processes (e.g., visitor check-in, maintenance request resolution, supply ordering)
- Error Rates: Track the frequency of administrative errors requiring correction
- First-Time Resolution Rate: Monitor the percentage of requests resolved without follow-up
- Response Time: Measure how quickly inquiries and service requests receive initial responses
Financial Performance Metrics
- Administrative Cost Per Employee: Calculate total administrative expenses divided by headcount
- Space Utilization Cost: Determine the cost per square foot based on actual usage patterns
- Resource Utilization Rate: Track the percentage of available resources (meeting rooms, equipment) being actively used
- Cost Avoidance: Measure savings from optimized processes and preventive maintenance
Employee Experience Metrics
- Workspace Satisfaction: Survey employees on their satisfaction with physical and digital work environments
- Service Quality Ratings: Collect feedback on administrative service quality
- Net Promoter Score: Measure likelihood of employees to recommend the workplace to others
- Friction Points Index: Track the frequency and severity of administrative pain points reported
Strategic Impact Metrics
- Workplace Enablement Score: Measure how effectively the workplace supports different work activities
- Collaboration Index: Track cross-departmental collaboration frequency and quality
- Innovation Support Rating: Assess how well the workplace environment enables innovation
- Talent Attraction/Retention Impact: Correlate workplace factors with recruitment and retention outcomes
Implementation Tool: Office Management Scorecard
|
Metric Category |
Key Metrics |
Current Performance |
Target |
Improvement Actions |
|
Operational |
Process cycle times, error rates |
X |
Y |
Process redesign, automation |
|
Financial |
Cost per employee, utilization rates |
X |
Y |
Space optimization, vendor consolidation |
|
Experience |
Satisfaction scores, friction reports |
X |
Y |
Service improvements, training programs |
|
Strategic |
Enablement score, collaboration index |
X |
Y |
Environment redesign, policy adjustments |
ROI Measurement Framework
Quantifying the return on investment for office management initiatives helps secure resources and demonstrate strategic value:
Direct Cost Savings
- Real Estate Optimization: Organizations adopting hybrid work models through effective space management report savings of up to 50% on office space expenses.
- Administrative Efficiency: Companies using office management software have achieved a 25% reduction in administrative costs through automation and streamlined processes.
- Technology Consolidation: Switching to integrated management platforms has saved organizations hundreds of thousands of dollars yearly by eliminating redundant systems.
Productivity Improvements
- Time Savings: Efficient office management systems reduce time spent on administrative tasks, with organizations reporting a rise in employee satisfaction ue to improved process efficiency.
- Reduced Interruptions: Streamlined request management and self-service options minimize workflow disruptions, contributing to focused work time.
- Faster Onboarding: Structured office management processes reduce time-to-productivity for new employees, with some organizations achieving a 30% reduction in onboarding time.
Risk Mitigation Value
- Compliance Management: Systematic record-keeping and process controls reduce compliance risks and potential penalties.
- Business Continuity: Robust office management systems ensure operational resilience during disruptions.
- Security Incident Reduction: Structured visitor management and access controls minimize security breaches.
Employee Experience Impact
- Retention Improvement: Organizations with effective office management systems report 15% higher retention rates.
- Attraction Enhancement: Well-managed workplaces become competitive advantages in recruitment.
- Engagement Increase: Removing administrative friction improves overall work satisfaction and engagement.
Conclusion: Building Effective Office Management
Effective office management serves as the operational backbone of successful organizations, integrating systems, spaces, and people into cohesive work environments that drive productivity and employee satisfaction. Throughout this comprehensive exploration, we've examined how office management has evolved from basic administrative oversight to a strategic function encompassing technology integration, experience design, and operational optimization.
Key Takeaways for Implementation
To build effective office management practices in your organization, focus on these essential elements:
- Systematic Approach: Apply the six key functions—planning, organizing, staffing, directing, controlling, and coordination—as an integrated framework rather than isolated activities. Organizations that view these functions holistically achieve greater operational coherence and efficiency.
- Strategic Technology Deployment: Select and implement office management solutions based on your specific organizational needs, ensuring they integrate smoothly with existing systems and processes. Remember that technology should solve real problems, not create additional administrative burdens.
- People-Centered Design: Develop office management practices that enhance the employee experience while achieving operational objectives.
- Data-Informed Decisions: Establish measurement systems that provide actionable insights into workspace utilization, resource allocation, and operational efficiency.
- Continuous Adaptation: Recognize that office management must evolve alongside organizational needs and workplace trends. Regular assessment and refinement of practices ensure continued relevance and effectiveness in changing environments.