Happy employees are five times more likely to stay with their organizations. While compensation plays a key role in employee motivation, the type of work environment you create has an equally significant impact on employee engagement, productivity, and business success.
According to Future Forum's 2023 report, 67% of workers prefer a hybrid work setup that blends remote and in-person work, allowing them to benefit from both in-office collaboration and at-home autonomy. This underscores the critical importance of creating work environments that foster both productivity and employee satisfaction.
What types of work environments can organizations build? And why are they so crucial for business success? This article explores distinct work environment types, provides real-world examples and case studies, and offers guidance on selecting the right environment for your organization's needs.
TL;DR:
- Happy employees are 5× more likely to stay, and the work environment plays a major role alongside compensation.
- 67% of workers prefer a hybrid model that blends remote flexibility with in-person collaboration.
- Work environments include both physical space (layout, location, equipment) and cultural factors (communication, leadership, inclusion).
- Different types of environments—like traditional, flexible, hybrid, creative, and agile—fit different company needs and goals.
- Physical elements such as office layout, amenities, and tech tools directly affect employee satisfaction and productivity.
- Toxic environments show up through poor communication, high turnover, and lack of psychological safety.
- Leadership behavior strongly shapes the work environment, especially through transparency and support.
- Technology like YAROOMS helps manage hybrid schedules, space usage, visitor access, and workplace analytics.
- The most effective work environments balance structure and flexibility while continuously adapting to employee needs.

Work Environment Defined
A work environment encompasses both the physical space and psychological conditions that employees experience in the workplace. It's shaped by numerous factors including office layout, communication styles, interpersonal relationships, organizational culture, and leadership approaches.
Every organization has its own unique work environment that evolves over time. While there are certain universal principles for healthy environments, successful organizations recognize that creating the right environment requires understanding their specific industry demands, employee needs, and organizational goals.
Key Elements of a Work Environment
Work environments comprise multiple interconnected components that together create the employee experience. These elements fall into two major categories: physical aspects and cultural aspects.
Physical Environment
Location
The location of your office space significantly impacts employee satisfaction and productivity. Proximity to public transportation, amenities, parking, and residential areas affects commute times, work-life balance, and employee punctuality. Recent data shows that 91% of workers indicated they could be persuaded to come into the office if the right benefits were offered, with shorter commutes (28%) ranking as the second most desirable incentive.
Size and Layout
The right office size and layout directly influence collaboration, focus, and overall employee well-being. Excessively cramped spaces create stress and disorganization, while overly large offices can foster isolation. Notably, only 47% of employers and 42% of employees globally believe their office spaces are adequately equipped to support the evolving needs of hybrid work, highlighting significant opportunities for improvement.
Equipment and Furnishings
While expensive furniture isn't necessary for a productive environment, ergonomic, comfortable, and functional equipment significantly impacts employee well-being and performance. Recent data indicates that 18% of employees cite better technology as a key incentive that would motivate them to come to the office more frequently, underscoring the importance of appropriate tools and equipment.
Facilities
Office amenities like bike storage, shower facilities, wellness rooms, cafeterias, and relaxation areas contribute significantly to employee satisfaction. These facilities demonstrate organizational commitment to employee well-being and can become important differentiators in talent attraction and retention.
Cultural Elements
Code of Conduct
Clear behavioral expectations documented in a code of conduct or employee handbook establish the foundation for workplace interactions. This documentation sets parameters for professional behavior, conflict resolution, and organizational values that shape daily experiences.
Accountability and Autonomy
Striking the right balance between accountability and autonomy is essential for employee motivation. Too much oversight stifles creativity, while insufficient guidance creates uncertainty. Organizations must calibrate this balance based on roles, experience levels, and organizational maturity.
Communication
Effective communication frameworks determine how information flows throughout the organization. This includes communication channels, feedback mechanisms, meeting protocols, and decision-making transparency. Poor communication creates confusion and erodes trust, while effective communication builds alignment and engagement.
Leadership and Development
Leadership style and development opportunities significantly shape workplace experience. Organizations that invest in leadership development and provide clear growth paths demonstrate commitment to employee advancement. The decline in employee wellbeing since its peak in 2022, with older managers and female managers experiencing the most significant decreases, highlights the importance of supporting leadership at all levels.
Diversity and Inclusion
Organizations that prioritize diversity and foster inclusive environments benefit from broader perspectives, increased innovation, and stronger employee engagement. Inclusion practices must extend beyond hiring to encompass advancement opportunities, decision-making inclusion, and equitable treatment.

Types of Work Environments
Understanding the different types of work environments can help organizations create spaces that align with their values, industry needs, and employee preferences. Here are ten distinct work environment types, with examples of organizations that have successfully implemented each approach:
1. Traditional (Conventional) Work Environment
Traditional work environments feature clear hierarchies, structured processes, and typically fixed hours (often 9-to-5). These environments emphasize formality, established procedures, and in-person work.
Characteristics:
- Fixed work schedules and locations
- Formal dress codes and communication styles
- Clearly defined reporting structures
- Physical office-based work
- Emphasis on face-to-face interactions
Example: A leading firm in the financial services industry upholds a traditional work model, requiring most employees to be in the office five days a week. Leadership believes that physical presence is essential to maintaining an apprenticeship-based culture and delivering strong client service.
2. Flexible Work Environment
A flexible work environment provides employees with options regarding when, where, and how they work. This approach prioritizes results over rigid processes, allowing customization based on individual needs and preferences.
Characteristics:
- Adaptable work schedules
- Options for remote or in-office work
- Focus on outcomes rather than hours worked
- Employee empowerment in workflow management
- Trust-based management approach
Example: A prominent company in the technology sector has embraced workplace flexibility through a model that allows employees to choose where they work based on their roles and individual needs. This approach has contributed to high employee satisfaction and enabled the organization to broaden its global talent pool.
3. Remote Work Environment
Remote environments eliminate geographic constraints by enabling employees to work from any location. These environments rely heavily on digital communication tools and require intentional approaches to maintain connection and culture.
Characteristics:
- Location independence
- Digital-first communication
- Self-directed workflow management
- Emphasis on results and deliverables
- Virtual collaboration tools
Example: A well-known organization in the software development industry operates as a fully remote company, with over 1,300 team members distributed across more than 65 countries. Its remote work practices are thoroughly documented in a comprehensive public handbook, which has become a widely referenced resource for implementing effective remote work strategies.
4. Hybrid Work Environment
Hybrid work environments blend in-office and remote work, offering flexibility while maintaining opportunities for in-person collaboration.
Characteristics:
- Combination of remote and in-office work
- Scheduled in-office days for team collaboration
- Digital and physical workspace optimization
- Flexible scheduling within parameters
- Focus on both individual and collaborative work
Case Study: A major player in the tech industry adopted a hybrid work model in 2022, requiring employees to be in the office three days per week while granting teams some flexibility in scheduling. The organization made significant investments in collaborative office environments and technology to enhance hybrid interactions. As a result, project-based teams saw productivity gains, employee engagement scores improved, and retention rates in key technical roles increased compared to the previous year. Internal surveys indicated that a majority of employees valued the added flexibility, with 80% reporting enhanced well-being and better work-life balance due to the hybrid approach.
5. Collaborative Work Environment
Collaborative environments prioritize teamwork, idea-sharing, and cross-functional cooperation. These spaces are designed to facilitate interaction and joint problem-solving.
Characteristics:
- Open floor plans or team-based layouts
- Abundant meeting and project spaces
- Emphasis on knowledge sharing
- Cross-functional teaming
- Collective decision-making processes
Example: A leading company in the animation industry designed its headquarters with the intentional goal of maximizing "unplanned collaborations." The layout features central communal areas where employees from various departments naturally cross paths throughout the day, fostering spontaneous interactions that drive creativity and innovation. This design philosophy was championed by a key visionary behind the company's growth.
6. Creative Work Environment
Creative work environments are designed to stimulate innovation, imagination, and artistic expression. These spaces often feature unconventional designs, flexible spaces, and abundant resources for experimentation.
Characteristics:
- Inspirational physical spaces
- Freedom to experiment and take risks
- Flexible project structures
- Emphasis on ideation and innovation
- Play and exploration encouraged
Example: A global technology company has outfitted its offices with playful and imaginative designs, including slides between floors, themed meeting rooms, and dedicated relaxation areas. These creative environments are a reflection of the company’s commitment to fostering innovation, encouraging out-of-the-box thinking, and supporting a dynamic workplace culture.
7. Agile Work Environment
Agile work environments support rapid iteration, continuous improvement, and adaptable team structures. These environments emphasize speed, flexibility, and customer-focused development.
Characteristics:
- Adaptable team configurations
- Rapid prototyping and feedback cycles
- Visual workflow management
- Continuous learning culture
- Customer or end-user centricity
Example: A leading company in the music streaming industry has implemented the "Squad Framework," an agile organizational model featuring autonomous, cross-functional teams—known as squads—that focus on specific aspects of the user experience. These squads coordinate through larger groupings called "tribes" and shared interest communities known as "guilds," allowing for both team independence and organizational alignment.

8. Sustainable/Green Work Environment
Sustainable work environments prioritize environmental responsibility, resource conservation, and employee wellness. These spaces minimize ecological impact while promoting health and well-being.
Characteristics:
- Energy-efficient facilities
- Waste reduction practices
- Natural elements and biophilic design
- Non-toxic materials and air quality management
- Support for sustainable employee behaviors
Example: A well-known company in the outdoor apparel industry has designed its headquarters to reflect a strong commitment to sustainability. The facility features solar panels, recycled building materials, natural ventilation systems, and an on-site cafeteria offering organic meals sourced from local farms, all contributing to environmentally responsible operations and employee well-being.
9. Activity-Based Work Environment
Activity-based work environments feature diverse spaces designed for specific work activities. Employees choose appropriate settings based on their current tasks rather than having assigned desks.
Characteristics:
- Variety of workspaces (focus rooms, collaborative areas, social spaces)
- No permanently assigned desks
- Freedom to move throughout the day
- Technology that supports mobility
- Task-appropriate settings
Example: A major firm in the professional services industry pioneered activity-based working at its Amsterdam office, offering a range of environments tailored to different tasks. These include quiet zones for focused work, collaborative spaces for team projects, and social areas for networking and informal interaction. The model is supported by advanced mobile technology, enabling employees to work flexibly and efficiently throughout the space.
10. High-Performance Work Environment
High-performance environments focus on excellence, achievement, and measurable results. These spaces often combine intense productivity expectations with substantial support and resources.
Characteristics:
- Clear performance metrics and goals
- Competitive yet supportive culture
- Emphasis on continuous improvement
- Recognition and reward systems
- Access to advanced tools and resources
Example: A leading aerospace company fosters a high-performance work environment characterized by ambitious goals, fast-paced development cycles, and a strong focus on innovation. While the demands are intense, the organization’s mission-driven culture appeals to highly motivated individuals who are drawn to making impactful contributions to cutting-edge advancements in space technology.
Comparison of Work Environment Types
When selecting a work environment model, organizations should consider various factors including industry requirements, organizational goals, and employee preferences. The following comparison table highlights key considerations for each work environment type:
|
Environment Type |
Ideal For |
Pros |
Cons |
Best Suited Industries |
|
Traditional |
Highly regulated industries, security-sensitive work |
Clear structure, established processes, in-person supervision |
Limited flexibility, potential for bureaucracy, higher real estate costs |
Finance, Healthcare, Government, Legal |
|
Flexible |
Knowledge work, service industries |
Improved work-life balance, higher employee satisfaction, broader talent access |
Potential coordination challenges, requires strong communication systems |
Technology, Marketing, Professional Services |
|
Remote |
Digital-first companies, global organizations |
Cost savings on facilities, global talent access, elimination of commutes |
Potential isolation, communication barriers, culture-building challenges |
Software Development, Content Creation, Customer Support |
|
Hybrid |
Most medium to large organizations |
Combines benefits of in-person and remote work, adaptable to changing needs |
Complexity in managing dual environments, potential inequity between remote and in-office staff |
Professional Services, Education, Technology |
|
Collaborative |
Project-based work, innovation-focused organizations |
Enhanced creativity, stronger team bonds, faster problem-solving |
Potential for distraction, challenges for introverted workers, can impede deep focused work |
Advertising, Design, Research and Development |
|
Creative |
Arts, design, innovation, product development |
Stimulates innovation, attracts creative talent, fosters unique solutions |
May feel chaotic to some, can be difficult to implement consistent processes |
Media, Design, Advertising, Entertainment |
|
Agile |
Software development, product development |
Faster delivery, customer-centricity, adaptability to change |
Requires significant cultural shift, may not suit all personality types |
Technology, Product Development, Manufacturing |
|
Sustainable/Green |
Organizations with ESG commitments, values-driven companies |
Reduced environmental impact, wellness benefits, alignment with growing consumer values |
Initially higher setup costs, requires ongoing commitment |
Consumer Goods, B Corp Organizations, Outdoor Industry |
|
Activity-Based |
Companies with diverse work styles and tasks |
Space optimization, supports different work modes, employee autonomy |
Transition challenges, requires significant change management, technology investments |
Consulting, Architecture, Creative Agencies |
|
High-Performance |
Goal-oriented, competitive industries |
Drives significant accomplishments, attracts ambitious talent, promotes excellence |
Risk of burnout, can create stress, may not suit all employees |
Technology Startups, Investment Banking, Management Consulting |
Identifying Toxic Work Environments
While understanding positive work environments is crucial, recognizing toxic workplace characteristics is equally important. Toxic work culture is 10 times more important than compensation in predicting employee turnover.
Warning Signs of a Toxic Work Environment
- Excessive turnover: High employee departure rates, especially among high performers, often indicate underlying workplace problems.
- Poor communication: Lack of transparency, information hoarding, and ineffective feedback mechanisms create confusion and erode trust.
- Pervasive negativity: Constant criticism, gossip, and cynicism signal a culture where positivity and growth are stifled.
- Unethical behaviors: Dishonesty, cutting corners, or pressure to compromise values indicate serious cultural issues.
- Work-life imbalance: Expectations of constant availability, shaming for taking time off, and burnout symptoms throughout the team reveal unsustainable practices.
- Lack of psychological safety: Environments where employees fear speaking up, making mistakes, or challenging ideas prevent innovation and growth.
- Favoritism and inequity: Inconsistent application of policies, unfair advancement opportunities, or special treatment damages trust and morale.
Addressing Toxic Work Environments
If you identify toxic elements in your work environment, consider these approaches:
- Conduct anonymous surveys: Gather honest feedback to understand the extent and nature of workplace issues.
- Review leadership behaviors: Toxic cultures often start from the top; leadership coaching or changes may be necessary.
- Implement clear policies: Establish and enforce guidelines around acceptable workplace behavior, communication, and conflict resolution.
- Create psychological safety: Actively encourage speaking up, dissenting opinions, and constructive feedback without fear of reprisal.
- Increase transparency: Share information openly about company decisions, performance, and expectations to build trust.
- Provide support resources: Offer mental health resources, stress management tools, and work-life balance support.
- Recognize and reward positive behaviors: Publicly acknowledge those who contribute to a healthy workplace culture.
The Impact of Work Environments on Healthy Work-Life Balance
A supportive work environment plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy work-life balance. According to a 2025 study, 84% of employees report being more productive in hybrid or remote settings compared to traditional office environments, highlighting how flexibility contributes to both balance and performance.
Work environments that promote balance typically feature:
- Reasonable work hours and respect for personal time
- Flexibility to accommodate personal responsibilities
- Clear boundaries between work and personal life
- Support for physical and mental wellness
- Recognition of life outside work
How Work Environments Impact Employee Experience and Productivity
The work environment directly influences how employees feel about their jobs and how effectively they perform. Consider these environment-productivity connections:
- Physical environment impacts: Insufficient natural light, poor air quality, and uncomfortable furnishings contribute to fatigue and reduced cognitive function. Conversely, ergonomic furniture, abundant natural light, and comfortable temperatures boost focus and energy.
- Cultural environment impacts: Rigid hierarchies and siloed departments hamper communication and innovation, while collaborative cultures with psychological safety encourage idea-sharing and problem-solving.
- Flexibility impacts: Research shows 84% of employees report increased productivity in hybrid or remote settings, highlighting the importance of allowing employees to work in their optimal environments.
- Inclusion impacts: Organizations with diverse and inclusive cultures experience higher productivity, as employees bring their full capabilities and perspectives to their work.
- Technology impacts: Outdated or inadequate technology creates friction in workflows and increases frustration, while appropriate digital tools enable efficiency and effectiveness.
These examples illustrate how intentionally designed work environments can transform employee experience and organizational results. By understanding the specific environmental factors that impact your workforce, you can create conditions that optimize both well-being and productivity.
What Type of Work Environment do Employees Prefer?
Employee preferences for work environments vary based on individual factors, generational differences, role requirements, and personal circumstances. According to Future Forum's 2023 report, 67% of workers prefer a hybrid work setup that blends remote and in-person work, allowing them to benefit from both in-office collaboration and at-home autonomy.
While preferences vary, survey data consistently shows employees value:
- Flexibility and choice: The ability to influence when, where, and how work happens
- Purpose and meaning: Connection to organizational mission and impact
- Growth opportunities: Clear paths for development and advancement
- Recognition: Acknowledgment of contributions and achievements
- Psychological safety: Freedom to express ideas and make mistakes without fear
- Inclusion: Feeling valued for their unique perspectives and backgrounds
- Work-life integration: Ability to balance professional and personal responsibilities
- Physical comfort: Environments that support health and well-being
Organizations that succeed in creating preferred work environments typically take an employee-centric approach, gathering regular feedback and adapting policies to meet evolving expectations. With 37% of employees reporting they wish they worked in a different work environment that better aligns with their preferences, organizations have significant opportunities to improve alignment between workplace offerings and employee needs.
Creating a Positive Work Environment
Building a positive work environment requires deliberate action aligned with organizational values and employee needs. Here are practical strategies for cultivating positivity in your workplace:
Create Impactful Job Descriptions
Job descriptions provide candidates' first glimpse into your organizational culture. Ensure they accurately detail expectations while showcasing your company's values and culture. Beyond listing responsibilities and qualifications, explain how each role contributes to broader team goals and organizational mission.
Invest in Workplace Culture
Meaningful investment in workplace culture extends beyond material perks. Implement regular training sessions and workshops that promote collaboration, communication, and problem-solving. Create opportunities for team building and cross-departmental interaction that strengthen relationships and build trust.
Demonstrate Appreciation Consistently
Recognition remains one of the most powerful tools for building positive environments. Develop systematic approaches to acknowledging contributions through formal recognition programs, public appreciation during meetings, or personalized acknowledgments. Train managers to provide specific, timely recognition that reinforces desired behaviors and outcomes.
Trust Your Team
Foster autonomy by giving employees appropriate decision-making authority within their roles. Avoid micromanagement, which diminishes motivation and signals distrust. Set clear expectations and outcomes while allowing team members flexibility in how they achieve goals.
Trust Your Team
Prioritize retaining employees who positively influence company culture. These individuals often embody organizational values, mentor others, and contribute to a positive atmosphere. Recognize and empower these employees as cultural ambassadors who help shape and reinforce desired workplace norms.
Establish Flexible Work Policies
Develop clear policies that support flexibility while maintaining accountability. Document expectations regarding communication, availability, and performance within flexible arrangements. Ensure policies promote equity between remote and in-office employees while supporting business requirements.
Maintain Open Communication
Transparency fosters trust and engagement throughout the organization. Establish regular communication rhythms including team meetings, one-on-ones, and company-wide updates. Create multiple channels for employees to share feedback, ask questions, and contribute ideas.

Measuring Work Environment Effectiveness
To understand whether your work environment effectively supports organizational goals and employee needs, implement a measurement framework with relevant metrics and KPIs:
Productivity Metrics
- Employee Productivity Rate: Output generated by each employee within specific timeframes
- Task Completion Rate: Percentage of assigned tasks successfully completed on time
- Employee Utilization: Percentage of working time spent on productive tasks
- Quality of Work: Error rates, customer feedback, or peer reviews on work quality
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction Metrics
- Employee Net Promoter Score (eNPS): Likelihood employees would recommend your organization as an employer
- Engagement Survey Results: Regular measurement of employee sentiment and connection to work
- 360-Degree Feedback: Comprehensive input from managers, peers, and direct reports
- Employee Resource Group Participation: Level of involvement in community-building groups
Retention and Turnover Metrics
- Voluntary Turnover Rate: Percentage of employees choosing to leave the organization
- Employee Retention Rate: Percentage of employees remaining over a specific period
- New Hire Retention: Percentage of new employees staying beyond 90 days, 6 months, and 1 year
- Average Tenure: Typical duration employees remain with the organization
Diversity and Inclusion Metrics
- Representation Metrics: Diversity across different organizational levels and departments
- Inclusion Survey Results: Employee perception of belonging and psychological safety
- Pay Equity Analysis: Assessment of compensation fairness across demographic groups
Space Utilization Metrics
- Occupancy Rate: Percentage of total available space that is actively used during business hours
- Desk Utilization: Average percentage of desks used compared to total available desks
- Meeting Room Utilization: Frequency and duration of meeting room bookings versus availability
Square Footage per Employee: Average space allocated per person, often used to identify optimization opportunities - Peak Usage Times: Identification of busiest times for office or specific zones to guide scheduling or redesign
- Vacancy Rate: Percentage of unoccupied or unused workspace over a given period
- Flexible Space Usage: Utilization rates of shared spaces like hot desks, collaboration areas, or lounges
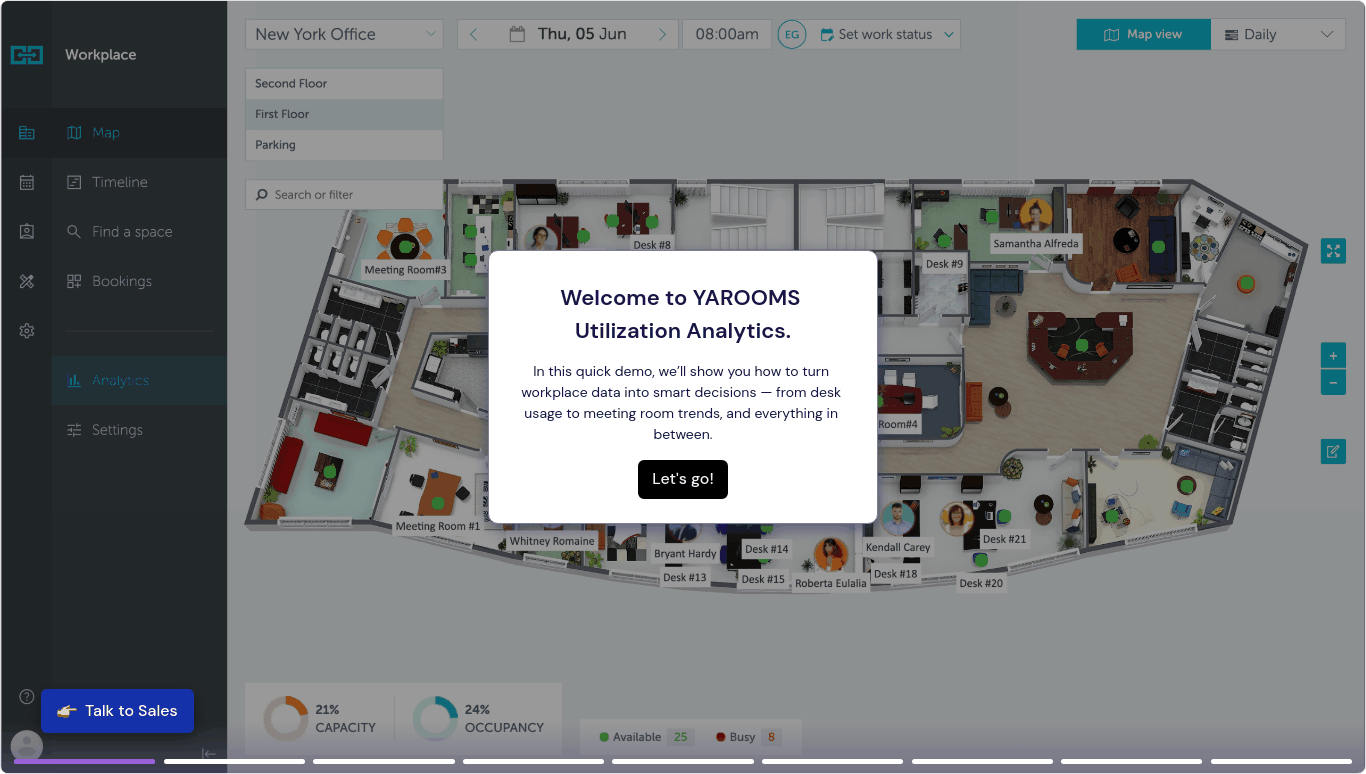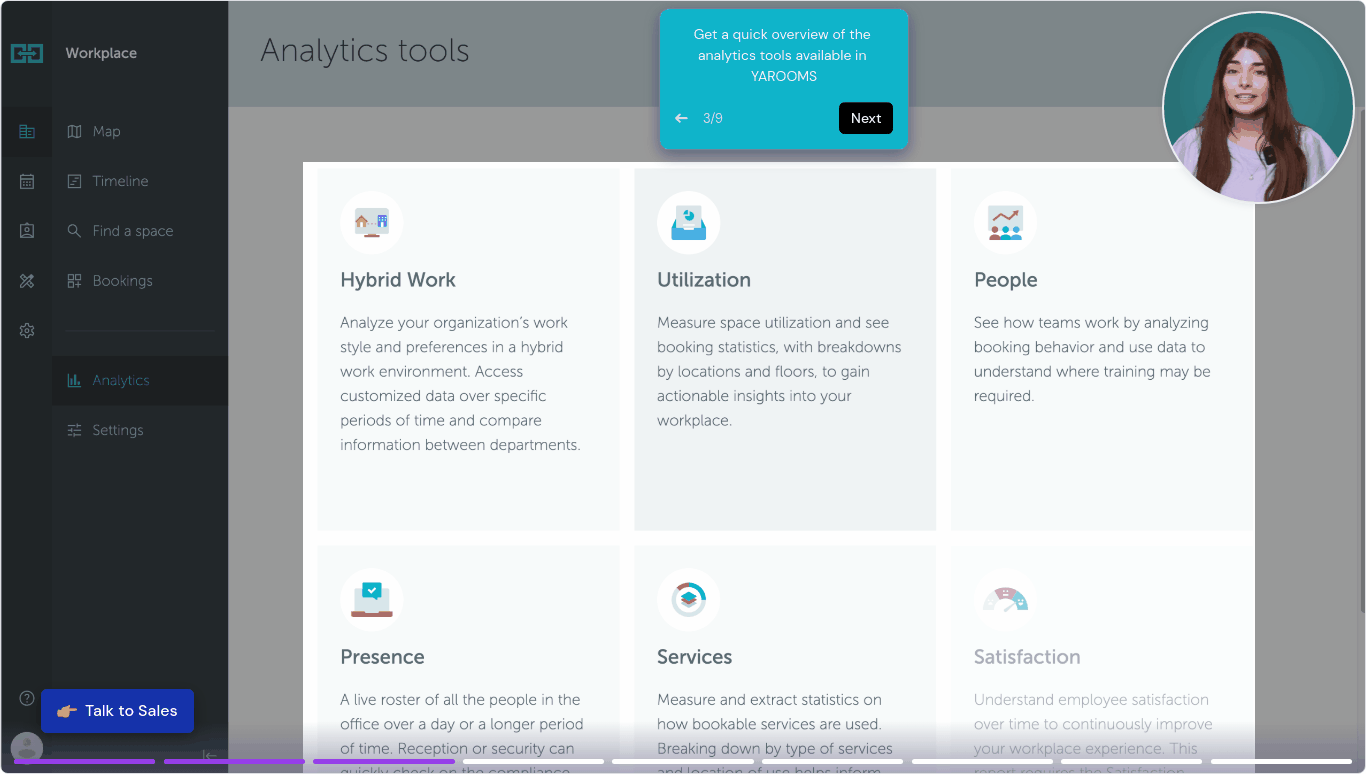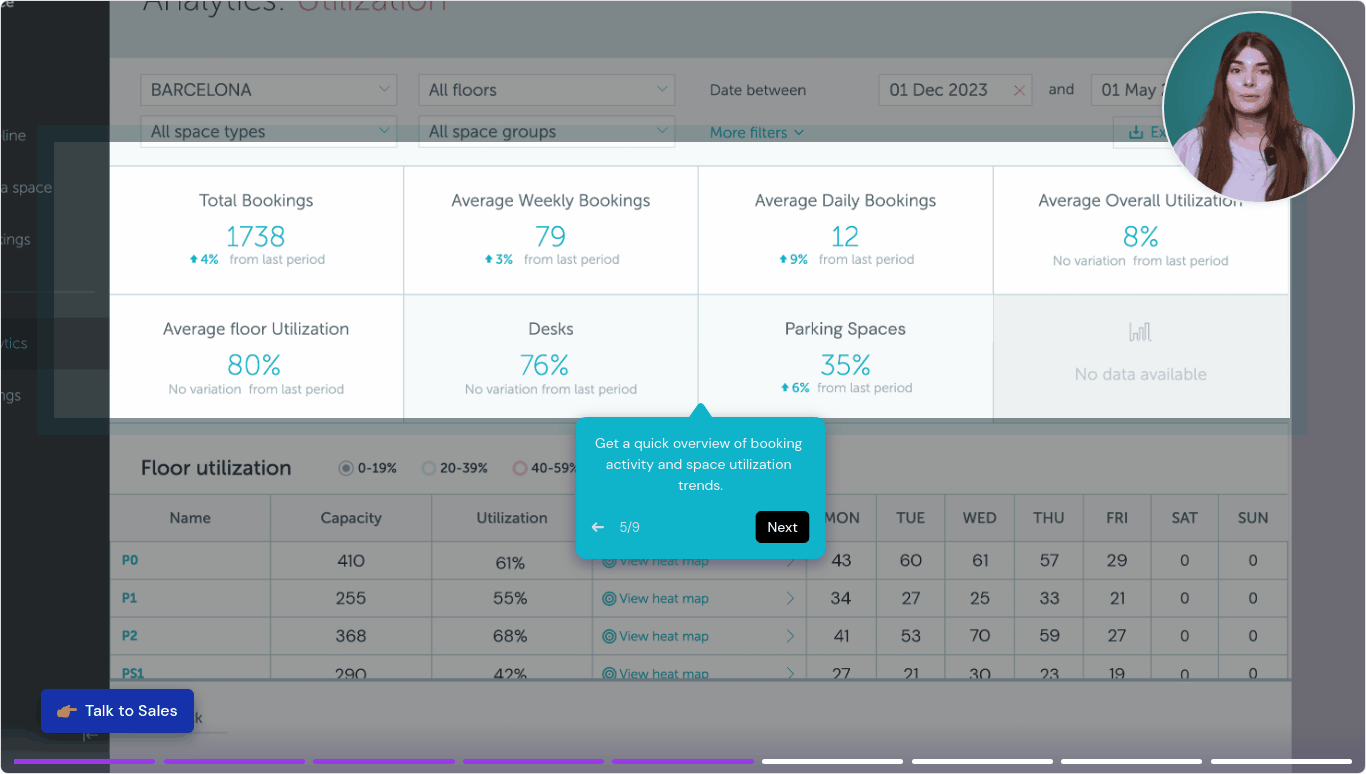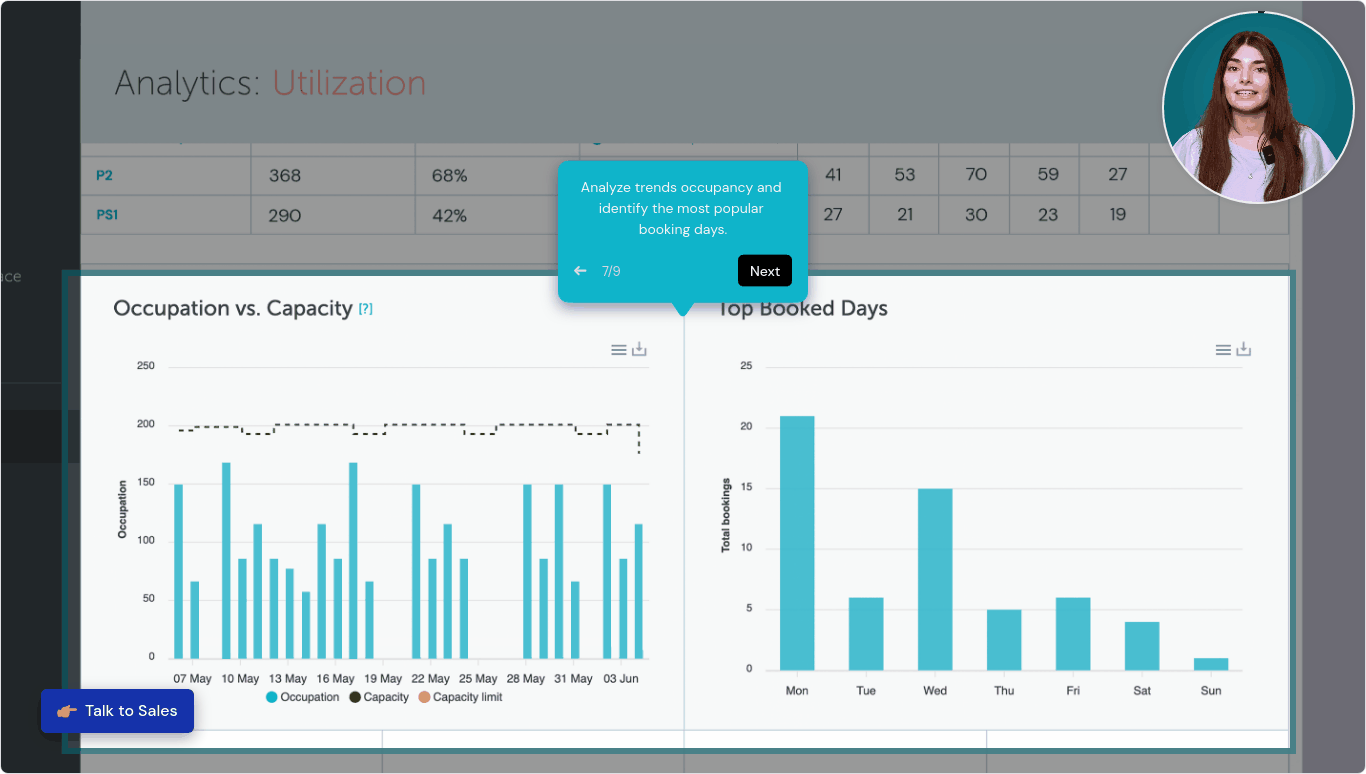
YAROOMS helps organizations track and improve space utilization by providing clear data on how workspaces are used. For example, it shows how often desks and meeting rooms are booked and actually used, helping identify underused areas. It also highlights peak usage times and occupancy trends, making it easier to adjust layouts or schedules to match real needs. This kind of insight supports better space planning, cost savings, and a more efficient work environment. Press the image below to see it in action:
The Role of Leadership in Shaping the Workplace Environment
Leadership significantly influences the workplace environment through behaviors, decisions, and priorities. Effective leaders shape positive environments through several key approaches:
Leading by Example
Leaders demonstrate desired workplace behaviors through their actions, not just words. When leaders embody organizational values like integrity, responsibility, professionalism, and empathy, these qualities proliferate throughout the organization. By modeling work-life balance, ethical decision-making, and respectful communication, leaders establish norms that others emulate.
Creating a Supportive and Inclusive Culture
Leaders build supportive cultures by fostering unity among team members and nurturing relationships characterized by mutual respect and psychological safety. They actively promote inclusion by ensuring diverse perspectives are heard and valued. As employee well-being has been declining since its peak of 35% in 2022, with older managers and female managers experiencing the most significant decreases, leadership support becomes increasingly crucial.
Promoting Employee Engagement
Effective leaders facilitate engagement by encouraging open communication, inspiring innovation, and creating opportunities for growth. They connect individual contributions to organizational purpose, helping employees see the impact of their work. Through meaningful delegation, appropriate autonomy, and regular coaching, leaders create conditions where employees feel motivated to contribute their best efforts.
Through these approaches, leadership shapes the workplace environment more powerfully than any policy or procedure. Organizations looking to transform their work environments must ensure leadership alignment and capability to drive the desired cultural changes.
Technology Solutions for Modern Work Environments
As work environments evolve, technology plays an increasingly critical role in supporting diverse work models. According to recent surveys, 75% of professionals agree that their companies' current technology needs improvement, while 72% believe their organizations need to invest in new technologies to effectively support flexible work models.
One-Stop Workplace Management Software
All-in-one workplace management platforms have become vital for organizations managing dynamic work environments. These solutions help optimize physical office space while supporting employee flexibility and collaboration.
Key capabilities include real-time occupancy tracking, space usage analytics, desk and meeting room booking, shared resource management, visitor management, hybrid work schedule calendars, and integration with digital signage for on-site visibility.
YAROOMS’ workplace management platform delivers all these features through an intuitive interface, enabling organizations to streamline hybrid work logistics, boost space efficiency, and enhance the overall employee experience.
AI and Automation Tools
Artificial intelligence and automation technologies are revolutionizing hybrid work environments by streamlining workflows and enhancing collaboration regardless of employee location.
Implementation areas include:
- AI-powered scheduling and project management
- Real-time transcription services for meetings
- Intelligent assistants for routine tasks
- Automated IT management and system monitoring
These technologies are expected to become deeply integrated into remote work ecosystems, allowing employees to focus on higher-value tasks while routine operations are handled automatically.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Platforms
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) technologies are being adopted to enhance remote collaboration and create more immersive meeting experiences. These technologies help bridge the gap between in-office and remote workers by creating shared virtual environments.
These technologies enable teams to collaborate in virtual spaces that simulate in-person interactions, potentially addressing one of the primary challenges of hybrid work: maintaining team cohesion and creative collaboration.
Organizations that successfully implement these technology solutions will likely gain advantages in talent recruitment and retention, as flexible work arrangements supported by effective technology are becoming increasingly important to the workforce.
The Future of Workplace Environments
Workplace environments continue to evolve in response to technological advancement, shifting employee expectations, and broader societal trends. Understanding emerging directions helps organizations prepare for future workplace needs.
Impact of Technology on the Workplace Environment
Technology continues to reshape work environments in profound ways:
- AI and automation are transforming job roles, eliminating repetitive tasks while creating new responsibilities focused on creativity, judgment, and human interaction
- Advanced collaboration tools enable seamless teamwork regardless of location, supporting distributed teams while reducing the necessity for constant physical presence
- Workplace analytics technologies provide unprecedented insights into space utilization, collaboration patterns, and productivity factors, enabling data-driven workplace decisions
- Wellness technologies from air quality monitors to circadian lighting systems are becoming standard elements of health-focused work environments
Adapting to Changing Employee Expectations
Employee expectations continue to evolve, with several clear trends emerging:
- Purpose-driven work environments that connect daily activities to meaningful impact are increasingly expected, particularly by younger generations
- Personalization of work arrangements, benefits, and development opportunities is becoming the norm rather than the exception
- Wellness integration beyond traditional benefits programs, with environments designed to support physical, mental, and emotional health
- Lifelong learning cultures that provide continuous growth opportunities throughout employees' careers
The gap between employee expectations and organizational delivery remains significant, with only 51% of employees feeling their organizations are meeting the promised experience regarding care, compassion, and connection that emerged during the pandemic. Organizations that anticipate these shifts and proactively adapt their work environments will gain significant advantages in talent attraction and retention.
Case Study: Apple's Iterative Hybrid Model
Apple, like many tech companies, moved to remote work during the pandemic. By 2023, Apple instituted a hybrid model requiring employees in the office three days a week. This gradual transition helped the company maintain high productivity and retention levels according to public filings, with employee satisfaction regarding the hybrid model generally positive, though with some resistance from those preferring more flexibility. Apple's approach demonstrates how companies can evolve their work environments incrementally while maintaining performance and addressing diverse employee preferences.

Conclusion: What Makes an Effective Work Environment?
Creating an effective work environment requires understanding your organization's unique needs while incorporating established best practices. The most successful work environments:
- Align with organizational purpose and values, creating authentic experiences that reinforce what matters most to your organization
- Balance structure with flexibility, providing sufficient guidance while allowing appropriate autonomy and personalization
- Prioritize both well-being and productivity, recognizing that these goals complement rather than compete with each other
- Adapt to evolving needs, regularly reassessing effectiveness and making adjustments based on data and feedback
- Support inclusion and belonging, ensuring all employees can contribute fully and feel valued for their unique perspectives
By thoughtfully designing physical spaces, establishing supportive cultural norms, and implementing appropriate policies, organizations create environments where employees thrive and business results follow. In today's competitive talent landscape, the quality of your work environment may be your most powerful differentiator.
Remember that building an effective work environment is an ongoing journey rather than a destination. Regular assessment, willingness to experiment, and continuous improvement will ensure your workplace remains aligned with organizational goals and employee needs in an ever-changing world.
Organizations looking to optimize their work environment can benefit from YAROOMS' comprehensive workplace management platform, which provides the tools needed to create adaptable, efficient spaces that support today's diverse work styles.