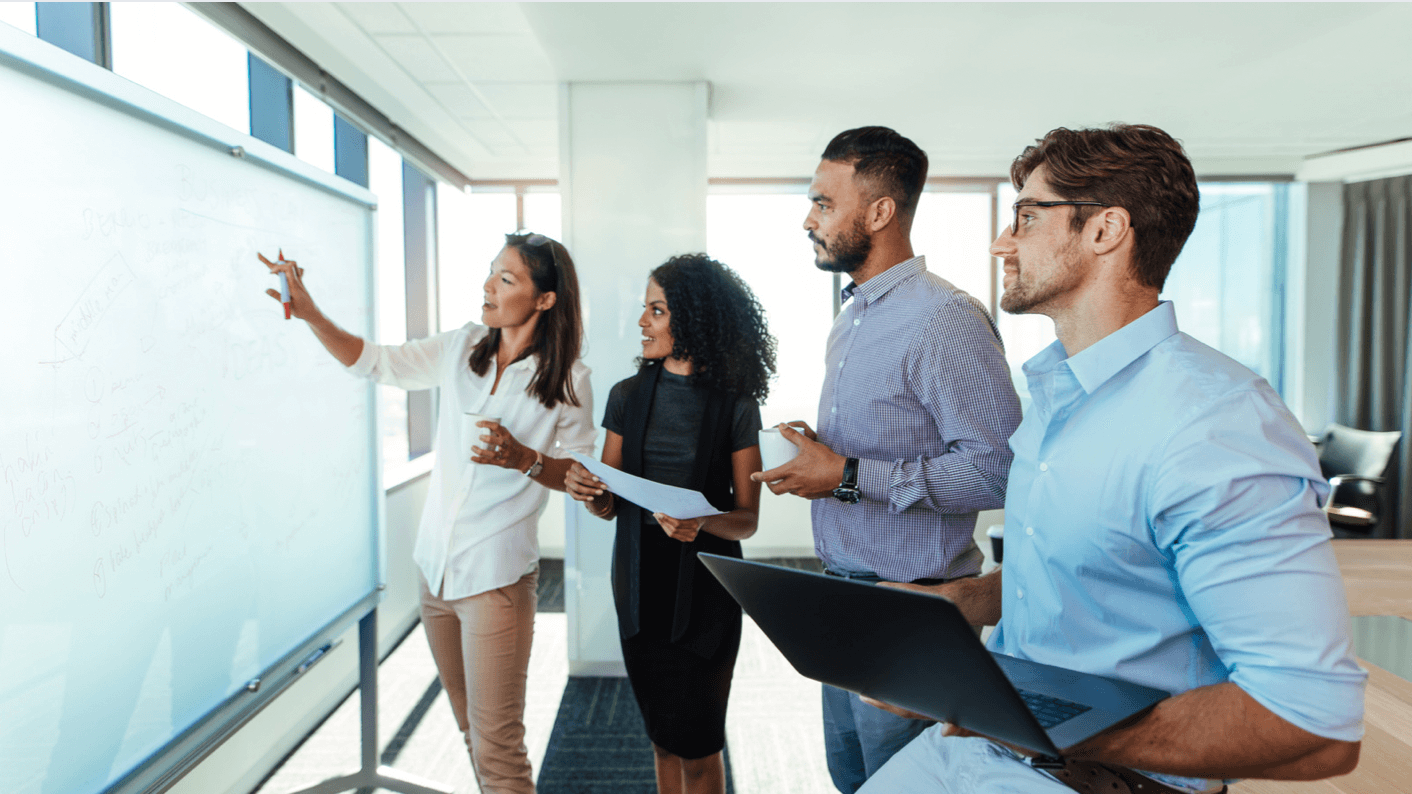
To survive and thrive, many organizations strive to become more Agile in their approach. They know that traditional organizations appear mechanical, hierarchical, and linear to younger generations (for example, did you know that 80% of today’s employees expect to work from home at least three times a week?) and hope that Agile ones feel more organic and better able to adapt to an unpredictable future. The nature of agility requires a high degree of flexibility, after all. Even the dictionary defines agility as "the ability to move quickly and easily." But what actually is an Agile work environment, and how do you create one?
TL;DR:
- An Agile work environment is designed for flexibility, optimal use of space and complete freedom of movement for employees.
- Agile is an iterative approach to project management that delivers tangible value in small chunks, refining the product and improving quality continuously.
- An Agile environment requires everyone to follow the values of individual and interactions, working software, customer collaboration, and responding to change.
- Three popular options for Agile work environments are activity-based working, office hoteling, and hot desking.
- Companies like Facebook, LinkedIn, Airbnb, and Salesforce have implemented Agile models, such as Google's Mountain View office.
- Agile methods provide many benefits, including customer satisfaction, improved quality, better control, adaptability, and predictability.
What is an Agile Work Environment?
By definition, an Agile work environment is a workplace that accommodates the changing needs of employees. Unlike a traditional office where employees are assigned a fixed workstation, an Agile work environment is designed for complete flexibility and optimal use of space by adopting a model of unassigned seating. Employees are encouraged to move freely around the office and work from the space that suits them best at any given moment.

Agile is an iterative approach to modern project management. Instead of focusing only on getting the product to market, such as in traditional project management, teams deliver tangible value in iterations or "smaller chunks”. This way, the project's risk and change management are done in real time. Each iteration is time-boxed and there is a value release at the end of each cycle. The product is therefore successively refined and its quality continuously improved.
Agile methods foster an open culture of collaboration that allows team members to learn from shared experiences and improve together, but only if the values that guide all processes and practises in an Agile environment are followed by everyone:
- Individuals and interactions
- Working software
- Customer collaboration
- Responding to change
With a network of cross-functional teams working together to deliver products and services that meet changing market expectations, Agile promises to deliver quickly, optimize resources, and maximize value. The first step in adopting the model is to create a foundation upon which flexibility, innovation and adaptability can thrive: the Agile environment.
Key Characteristics of an Agile Work Environment
An agile work environment fundamentally changes how businesses operate and interact with their employees. Rather than sticking to outdated hierarchies and processes, agility fosters adaptability, encourages collaboration, and empowers employees. Here are the key features that constitute an effective agile work environment:
- Employee Autonomy: An essential characteristic of an agile working system is autonomy granted to teams or individuals by allowing them to choose when, where, and how they fulfill their tasks based on their productivity patterns.
- Flexible Space Design: One size certainly does not fit all in an agile setting. Workspaces must cater to diverse needs ranging from quiet, solitary spaces for focused task completion to more extensive open areas ideal for promoting creative discussions.
- Active Collaboration: An agile workplace thrives on collaboration rather than competition. Platforms facilitating shared decision-making form an integral part of these environments.
- Fluid Roles: Hierarchical boundaries blur in such work settings, making roles fluid per project requirements, leading towards a truly multi-disciplinary approach.
- Leveraging Technology: With remote or hybrid working becoming normative, technology is pivotal in ensuring seamless collaboration across physical distances.
Types of an Agile Working Environment
An Agile environment fosters and supports a culture that encourages teams to collaborate, be flexible, embrace change, and adapt to changing demands. But how does that look?
The three most popular options for an Agile work environment are activity-based working (ABW), office hoteling, and hot desking. In an activity-based working (ABW) environment, employees can reserve workspaces throughout the day and move frequently from one location to another as their activities change. In office hoteling, employees can reserve a workspace before they arrive, ensuring that a desk is waiting for them. This gives employees a "home base”, improves space utilization and reduces real estate costs.

Hot desking refers to having unassigned desks, so that multiple people can use a given workstation. It works well in environments where not everyone needs to be in the office at the same time, provides a cost-effective use of space, and promises greater interaction between teams. However, it does require extensive wayfinding, as well as sufficient seating for days when everyone is in the office.
Types of Agile Workspaces
Agile work environments come in diverse forms, tailored to meet specific organizational and employee needs.
Open Plan Spaces: Advantages and Considerations
Open-plan spaces are a common feature of the modern agile working environment. They create a sense of unity, facilitate spontaneous interaction, foster better communication, and pave the way for deeper collaboration.
Ideally, employees aren't relegated to cubicles in such settings – they can move around freely, navigating their workspace as needed. This encourages active engagement with both the space itself and other team members. However, careful thought needs to go into designing open spaces that account for noise control and privacy considerations to maintain an effective working environment.
Quiet Zones: Creating A Focused And Productive Environment
Quiet zones within an agile workplace staffing system have been recognized for their importance in facilitating focus-driven tasks. Contrary to popular belief, not all work benefits from constant collaboration or discussion; some tasks require deep concentration or even solitude.
By dedicating specific areas for quiet work, companies allow employees to find solace amid the hustle of day-to-day operations—an essential aspect when working in an agile environment that often demands high levels of creativity and problem-solving skills.
Breakout Spaces: Encouraging Collaboration And Creativity
Breakout spaces are informal areas explicitly designed for relaxation and casual interactions—a vital characteristic of an agile work environment. These could be lounge-like corners with comfortable seating or strategically placed benches alongside windows offering picturesque views.
These spaces serve a dual purpose: they offer workers a place to unwind during breaks while encouraging idea-sharing outside traditional meeting rooms—cultivating innovation ingrained in the fabric of what it means to be agile in the workplace.
Resource Areas: Ensuring Accessibility And Convenience
Resource areas form another essential component of an agile workspace. Typically housing equipment like printers, scanners—and, on many occasions, coffee machines—these areas serve as hubs that bring people together and promote spontaneous interactions, which can spark innovative work-related discussions.
These areas must be conveniently located within the workplace. Accessibility reduces wasted time and boosts productivity—personifying what is agile working in its truest sense.
Touchdown Spaces: Flexibility For Remote Or Visiting Employees
Lastly, we have touchdown spaces. These are often temporary places where employees from remote locations—or even visiting clients—can easily "touch down" to catch up on work or participate in impromptu meetings.
In an era where remote working has become more frequent, such spaces play a vital role in maintaining connectivity and ensuring seamless collaboration—an embodiment of how to be agile at work despite geographical constraints. As with other aspects of the agile workspace, they demand thoughtful design for simplicity, comfort, and functionality.
Traits of an Agile Work Environment
An agile working environment is characterized by several key traits that foster flexibility, collaboration, and innovation.
One prominent feature is its emphasis on adaptability, where teams can swiftly respond to changing circumstances and evolving market demands. This adaptability is supported by an open communication and transparency culture, enabling employees to freely voice their ideas, concerns, and feedback.
Additionally, cross-functional collaboration is a cornerstone of an agile workspace, promoting the integration of diverse perspectives and skills to tackle complex challenges effectively. Such an environment also encourages experimentation and risk-taking, cultivating a mindset where failures are perceived as opportunities for learning and growth.
Moreover, agile workplaces often prioritize a results-oriented approach, valuing the achievement of concrete outcomes over traditional processes.
Finally, a solid commitment to continuous learning and development is fundamental, as employees are encouraged to constantly acquire new skills and knowledge to stay ahead in a rapidly changing business landscape.
Real-Life Examples of Working in an Agile Environment
Facebook, LinkedIn, Airbnb, Salesforce and other companies are implementing an Agile model as we speak (or read). Google's Mountain View office, for example, has workspaces with less space for individuals and more space for collective teams that supports co-creation of value. Shared tables in open areas actually invite more stand-up meetings, while project rooms on the periphery have tools for workshops. Teams can use dedicated team rooms with writable walls and areas for brainstorming!
Why Are Agile Workspaces So Popular? Benefits of Agile Working
More and more companies are recognizing the transformative benefits that this innovative suite of methods provides, such as:
Customer Satisfaction
In an Agile system, the customer is always involved in the decision-making process. The team delivers incremental value, solicits their feedback, and incorporates it into subsequent iterations, resulting in greater customer engagement. By involving the customer in the development process, the Agile team ensures that the final product truly meets their needs. In a traditional framework the customer is only involved in the planning phase and has no influence on the execution, which greatly affects flexibility and adaptability.
Improved Quality
The iterative approach means that processes are improved each time an interval is repeated. Testing is an indispensable part of the process after each sprint (basically, after the development of each feature or set of features), often executed through agile testing practices that align QA with development in real time. This consistent focus on improvement and quality control is one of the core principles of Agile and helps teams improve their processes, deliver value at every stage, and create high-quality products.
Better Control
Often, products developed using Agile methods are delivered faster. This is due to the prioritization of tasks in Agile. During development, the team breaks down the final product into smaller pieces to deliver a working product sooner, test it, and build on it later. This provides much more control due to transparency, integration of feedback, and continuous quality control of the project.
Adaptability
Agile gives projects unparalleled flexibility. The project is divided into short, manageable sprints that allow teams to make last-minute changes and adapt to constant feedback from the customer without causing major disruption. This means they can deliver consistently and meet changing customer needs effectively. With other project management methods, changes are typically time-consuming and costly.

Predictability
Agile teams work in short periods of time, which makes it easier for project managers to measure team performance and allocate resources accordingly. It's also easier to predict costs for shorter time periods than for a long-term project, simplifying the estimation process. Greater visibility makes it easier to identify and predict risks, develop effective mitigation plans, and ensure smooth project execution.
Reduced Risk
Agile methods are also a great framework for mitigating risk, as regular assessment of progress provides a better overview of the project and faster identification of potential obstacles that can be addressed before they escalate. This greatly increases the chances of project success. And because Agile focuses on the value delivered in each sprint, teams can respond to change more quickly compared to traditional teams.
Better Communication
Agile teams value continuous interaction. They typically hold daily meetings to ensure everyone is on the same page and working toward the same goals. From task definition and effort estimation to development, testing and release, the team is closely aligned to achieve common goals. And, because team size is limited, Agile provides an environment where teams have more flexible structures, leading to more creativity and innovation.
Common Challenges in Agile Workspaces
Changing the way an entire organization thinks and operates is not easy, so some challenges when adopting Agile are to be expected. They tend to fall into three categories:
Culture
Successful Agile adoption starts with a servant leadership mindset, where managers set strategic goals and then trust their teams to achieve them in the way that works best for them. Those accustomed to judging employees by how many hours they sit at their desks need to look past "presenteeism" and instead evaluate employee productivity and their contribution to the team.
Work Management
Traditional project management approaches assume a fixed scope and estimate the time and resources required to complete it. But in the Agile model, time and resources are defined by set iteration windows and teams of people, while scope becomes more fluid through constant learning and change. Teams experiment, get feedback quickly, and adjust scope accordingly. This allows organizations to adapt quickly.
Technology
Transitioning from a traditional office model with fixed workstations to an Agile work environment requires a massive culture shift, but don’t treat plans for the new Agile work environment as a top-secret project. Allow employees to get excited about the cool features they will enjoy in the new environment! Pay particular attention to technology and opt for solutions that connect teams and improve visibility and workflow.
Implementing an Agile Work Environment
An organization that wants to become Agile can start by creating an enabling environment that equips its people with the right physical infrastructure and tools. This can be done in a number of ways:
Bring the Team Together
Having teams in the same space at least some of the time builds trust, promotes communication and provides transparency. A workspace should offer enough open workstations where employees can gather together to collaborate more easily and help each other if they find themselves in a difficult situation.

Set up a Dedicated Space for the Team
Teams that are in the same place work better when they have their own space where they can collaborate in close proximity. Workstations around the perimeter of the room, a conference table in the middle, and a wall of whiteboards for taking notes, assigning tasks, etc. can increase productivity.
Protect the Team from Distractions
Any outside distractions will throw the team off track and significantly impede progress, so the Scrum Master should strive to remove obstacles that affect the team's focus. Teams should be working on one goal at a time, avoiding multitasking and distractions, and figuring out what the next best step would be.
Equip the Team with the Right Tools
While merging teams is not always an option, teams spread across different regions and time zones can take advantage of online collaboration tools to be on the same page and stay in touch in real time. Luckily there are many productivity-enhancing tools to help teams stay on schedule, on budget, and on resources.
YAROOMS, for example, is a comprehensive workplace platform that plays a pivotal role in supporting agile workplaces. It fosters seamless collaboration by offering advanced scheduling features that streamline the reservation of meeting rooms, desks, and other resources, promoting efficient utilization of space.
Furthermore, its intuitive interface and real-time data analytics empower organizations to make data-driven decisions, optimizing space usage and enhancing overall productivity.
YAROOMS integration capabilities with other workplace tools also contribute to creating a cohesive digital ecosystem, promoting smooth communication and strengthening the overall agility of the workplace.
Best Practices for Sustaining an Agile Work Environment
Let's discuss some of the best practices to ensure your journey into agility lasts long-term and continually reinforces positive change.
Regularly Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Agile Work Environment
One crucial practice in maintaining an agile work environment is regular evaluation. This involves measuring productivity levels, employee satisfaction, costs saved, and other key performance indicators (KPIs). Gauging what's working well and areas requiring adjustments helps shape a more effective agile workplace staffing strategy.
You could use quantitative methods, such as performance data—employee output or sales—and qualitative feedback via surveys or team meetings to better understand how your workspace impacts working dynamics. Remember, it's not precisely about finding problems but identifying opportunities for improvement.
Providing Ongoing Training and Support for Employees
Establishing a genuinely agile work environment goes beyond physically redesigning office spaces—it requires skill development, too. It’s integral to frequently provide training programs for employees to adapt efficiently to their new environments and responsibilities.
Offering consistent support and learning opportunities allows everyone to remain on top of their game within the dynamic pace set by agility.
Not only does this boost competence among staff members who may be evolving roles due to transitioning towards agility-optimized positions, but it also increases confidence across teams overall—a key ingredient in fostering productivity within any organization.
Encouraging Continuous Improvement and Feedback Loops
Optimally operating an agile workplace calls for implementations that encourage constant progress. The cornerstone here is creating an atmosphere conducive to open communication: discussing triumphs, struggles, and confusions. Make it safe for team members to suggest improvements without fear of negative backlash—this is the backbone of feedback loops and continuous improvement processes.
Not to mention, regular application of agile retrospectives encourages reviewing past projects, learning from them, and applying that wisdom to further tasks—an essential practice for ensuring the productive perpetuation of agility in your work environment.
Embracing Agile Principles Beyond Physical Workspace Design
Finally, a sustainable agile work environment is not only about the physical structures or practical mechanisms but also hinges on the mindset. Embrace agile thinking patterns beyond workspace design—make it part of your corporate culture.
It means fostering attitudes that embrace change, promote transparency, and champion individual strengths—all indicators of a healthy and thriving agile network. It could involve adopting different managerial approaches, empowering autonomy among team members, or even altering business practices to prioritize customer satisfaction.
The Future of Agile Work Environments
The future of agile work environments is a transformative journey, transcending the conventional notions of productivity and office structures. This shift towards agility signifies a departure from rigid schedules to task-based accomplishments, prioritizing employee well-being and work-life balance through inclusive design elements.
With the rise of globalization and remote work, cross-cultural agility assumes paramount importance, necessitating sophisticated digital infrastructure for seamless collaboration across diverse time zones.
Notably, the only constant in this evolving landscape is continual adaptation and improvement, as fostering an agile workspace requires a sustained commitment to iterative changes and a dedication to learning. While the future might unveil unexpected developments, the foundational principles of agility are poised to endure.